Screw Thread Insert (STI) taps are designed to cut oversized threads for helical coil inserts, which provide stronger, more durable threads and ensure balanced load distribution.
STI Taps: Types, Finishes, and Reference Guides
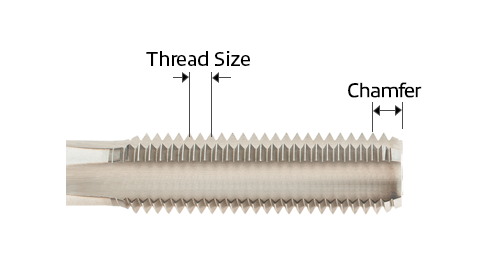
Diagram of a Screw Thread Insert (STI) Tap


Essential Tips
Types of STI Taps

Spiral Point STI Taps
Feature flute geometry that pushes chips forward, minimizing clogging and reducing load. Ideal for longer through and blind holes, but not recommended for abrasive materials.

Pipe STI Taps
Used to cut oversized internal threads in pipes and fittings for pressure-tight joints. Because pipe threads require 100% thread depth, they demand higher cutting forces than standard machine threads.

Thread forming STI Taps
Create internal threads by displacing metal rather than cutting, producing no chips—ideal for larger holes. They work well with aluminum, brass, copper, steel, and other soft metals, and are designed for holes tapped to screw thread standards.

Spiral Flute STI Taps
Feature a high helix angle that efficiently evacuates chips from aluminum, copper, and other soft materials. Ideal for tapping blind holes.
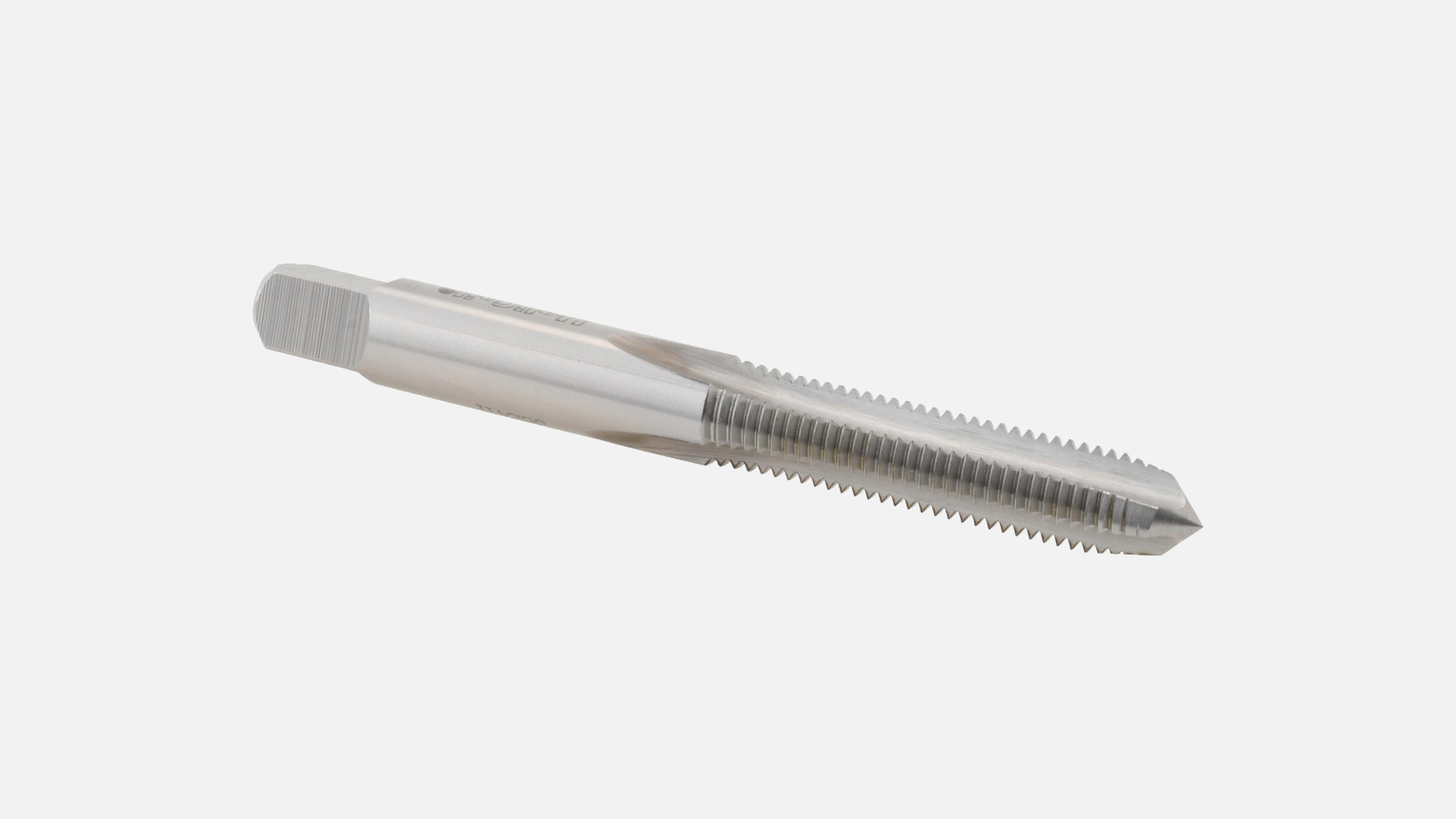

Hand STI Taps
Feature a flute design that pushes chips ahead of the cutting action, minimizing loading and clogging. Suitable for both hand and machine tapping in through and blind holes. Not recommended for abrasive materials.
Class of Fit & Thread Limits (H & D)

Class of Fit refers to the standard system used to specify the tolerance and precision of fit between a tap and a threaded hole. Unified threads use "A" for external and "B" for internal threads, while Metric threads use "G" for external and "H" for internal threads.
Example Applications:
• Class 1A & 1B – Designed for loose fits, allowing frequent and quick assembly and disassembly.
• Class 2A & 2B – Provide a medium fit to prevent seizure during assembly. Commonly used for general-purpose screws, bolts, and nuts.
• Class 3A & 3B – Precision threads with a tight fit, requiring gauges for accurate inspection. Ideal where high accuracy and minimal play are essential.
The Thread Limit refers to the tolerance range applied to a tap beyond its basic thread size. It is designated by “H” (inch) or “D” (metric), followed by a number. Thread limits allow selection of the tap size best suited to achieve the desired thread class.
The difference between H limits is 0.0005″ for taps up to 1″ diameter, and 0.001″ for sizes over 1 inch. Use lower H numbers (e.g., H1 or H2) if threads are too loose, and higher H numbers if threads are too tight. Selecting the correct H limit ensures threads stay within the specified tolerance on the part print.
Rule of thumb: Choose the largest H limit that still produces the required class of fit to maximize tool life.
Thread Limit (H & D) Cross Reference Guide
H1/D1 | Basic plus .0005" - .0010" |
H2/D2 | Basic plus .0005" - .0010" |
H3/D3 | Basic plus .0010" - .0015" |
H4/D4 | Basic plus .0015" - .0020" |
H5/D5 | Basic plus .0020" - .0025" |
H6/D6 | Basic plus .0025" - .0030" |
H7/D7 | Basic plus .0030" - .0035" |
H8/D8 | Basic plus .0035" - .0040" |
H9/D9 | Basic plus .0040" - .0045" |
H10/D10 | Basic plus .0045" - .0050" |
H11/D11 | Basic plus .0050" - .0055" |
H12/D12 | Basic plus .0055" - .0060" |

Chamfer Styles
• Bottoming chamfers, with 1 to 2 threads, are used to cut threads close to the bottom of blind holes.
• Modified bottoming chamfers are longer than standard bottoming chamfers and have more threads—typically 2 to 2.5. They're used for threading closer to the bottom of blind holes.
• Taper chamfers, or starter taps, have 7 to 10 threads and a long chamfer for a gentle, less aggressive cutting action.
• Plug chamfers, the most commonly used type, have 3 to 5 threads and are suited for efficiently threading both through and blind holes.
• Semi-bottoming chamfers, with 3 to 3.5 threads, are used for threading blind holes.

Standard Finishes
• Bright finish provides a smooth, polished surface that enhances chip flow in soft materials like aluminum, wood, and plastic.
• Titanium Nitride (TiN) is a versatile coating that improves chip flow in soft materials. Its heat and wear resistance allow for higher cutting speeds than uncoated tools.
• Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) is harder and more wear-resistant than TiN. It is used on stainless steels, cast iron, and aluminum alloys.
• Oxide, also called black or steam oxide, is a surface treatment that reduces chip buildup, galling, and welding. It's commonly used on low-carbon steel, stainless steel, and other ferrous metals.
• Nitride is a thin, hard coating that enhances surface hardness and is ideal for abrasive or high-wear applications.
Inserts Used with STI Taps
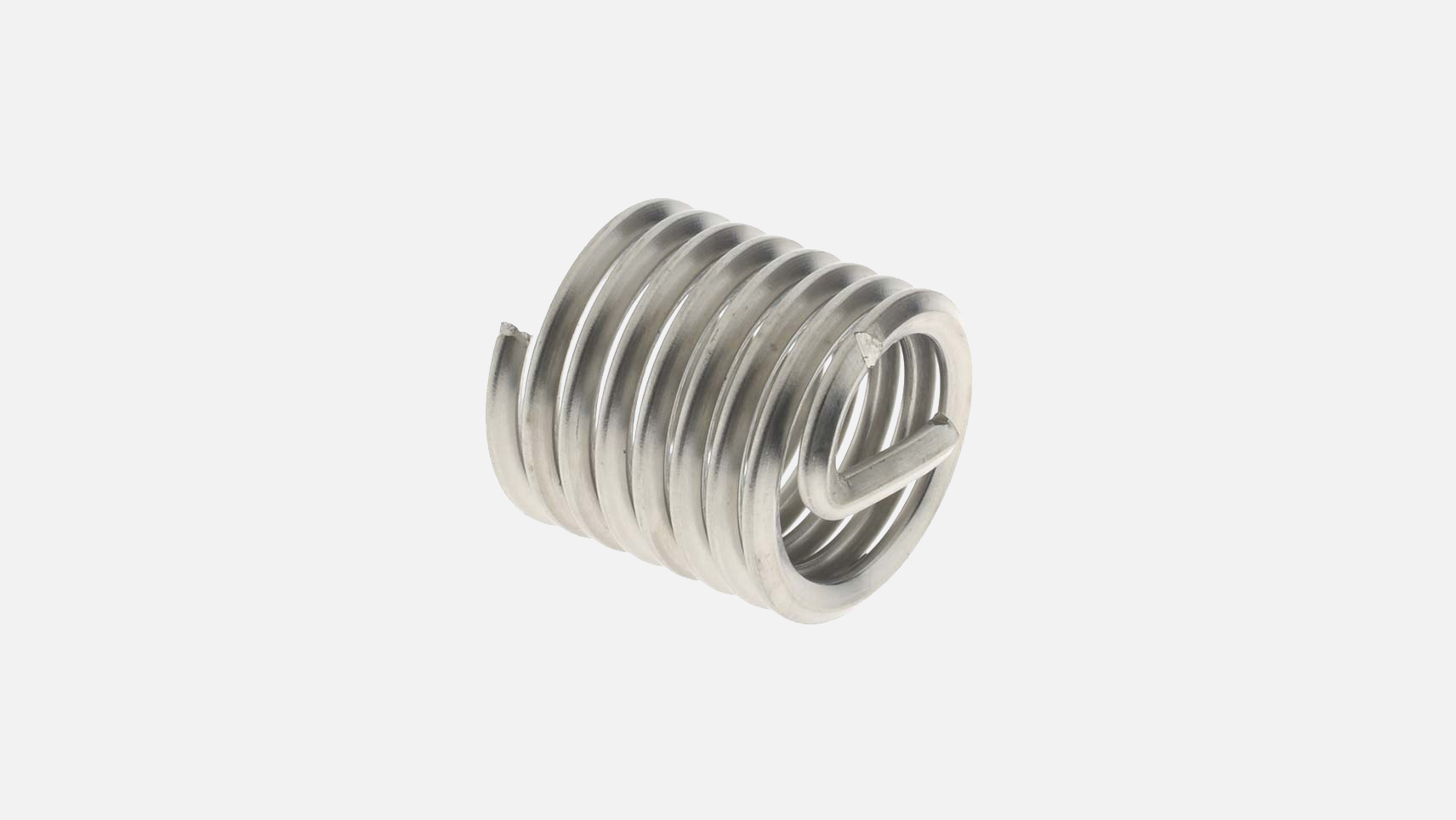

Free-Running Inserts
Are coils used to repair tapped holes that have been stripped due to wear, corrosion, or over-torque.

Thread-Locking Inserts
Restores worn, damaged, or stripped threads. An adhesive or nylon locking element on the external threads secures them in place and seals against liquids and gases.
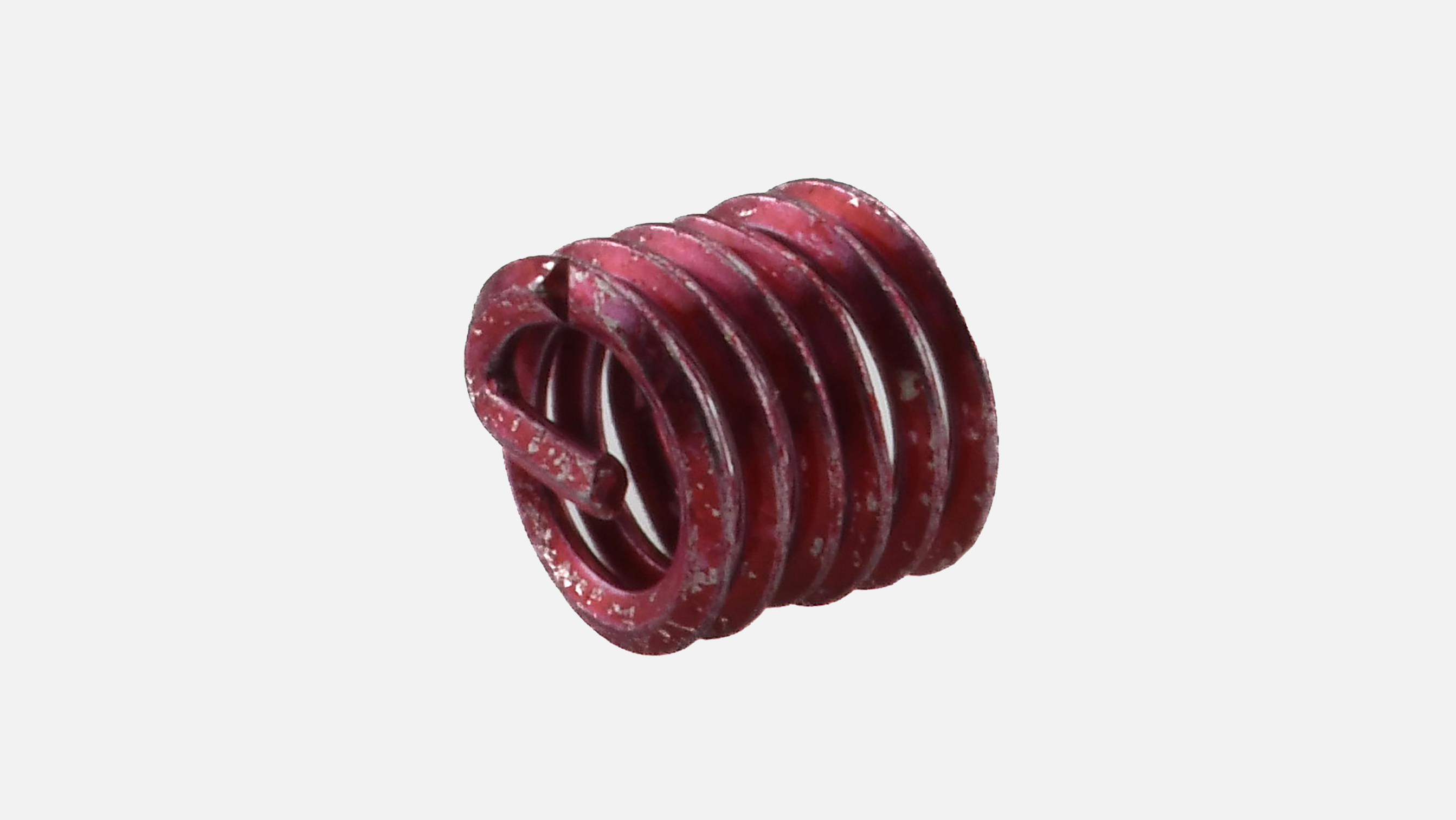

Screw-Locking Inserts
Restores worn, damaged, or stripped threads. Built-in locking coils grip screws or bolts to prevent loosening from vibration, eliminating the need for additional locking methods.

