Choosing Depressed Center Grinding Wheels
Depressed center wheels are a versatile type of grinding wheel used for stock removal, blending, grinding, cutting, notching, and deburring. The recessed or “depressed” center allows clearance for mounting hardware so the wheel can be used flat against a surface without interference.
These wheels are designed for right-angle grinders and are available with or without a hub. Due to their shape, they offer strength, stability, and flexibility for a wide range of applications.
Wheel Thickness & Applications
The thickness of a depressed center wheel determines how it should be used:
1/4" thick wheels: Built for grinding only. Their thickness provides the durability needed for heavy stock removal.
Less than 1/8" thick wheels: Designed strictly for cutting and notching, where a thinner wheel produces a faster, cleaner cut.
Exactly 1/8" thick wheels: Known as combination wheels. They can handle light grinding while also cutting effectively.
Tip: Always match the wheel thickness to the job. Using a cutting wheel for grinding can be unsafe.
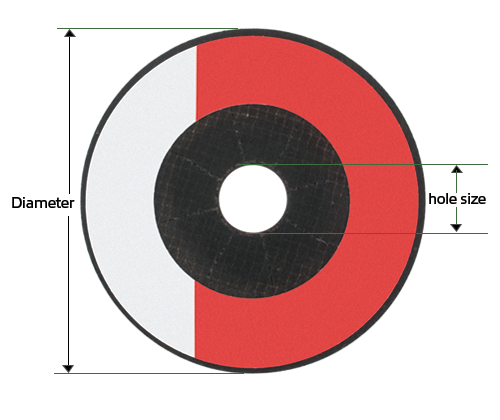
Diagram of a Depressed Center Wheel
Center Wheel Grit & Grade Selection
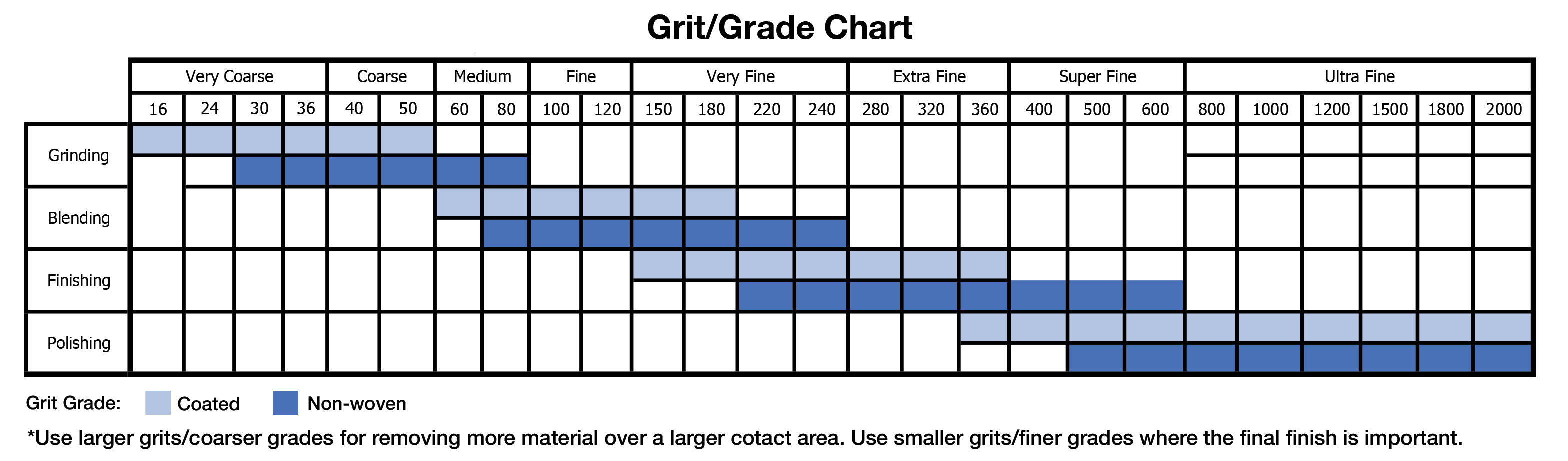
The grit size of a wheel affects both the aggressiveness of its cut and the quality of the finish.
- Coarse grits (16–60): Best for fast material removal and heavy grinding.
- Medium to fine grits (80–220): Used for blending and intermediate finishing.
- Very fine to extra fine (240–600): Chosen for finishing where surface quality matters.
- Super fine to ultra fine (800–2000): Designed for polishing and creating extremely smooth finishes.
Types of Depressed Center Wheels

Type 27 Wheels
- Flat grinding face
- Designed for side grinding and general surface work

Type 28 Wheels
- Convex or “saucer” shape
- Allows better access for corner and side grinding
- Not recommended for cutting or notching

Type 29 Wheels
- Concave or “reversed saucer” shape
- Designed for blending and stock removal that leaves a smoother finish
- Not recommended for cutting or notching
Abrasive Materials for Depressed Center Wheels
Aluminum Oxide
Most common abrasive grain
Economical, tough, and fracture-resistant
Best for ferrous alloys, high-tensile steels, and wood
Aluminum Oxide / Silicon Carbide Blends
More durable than aluminum oxide alone
Used on steel parts with scale and iron castings
Ceramic
High-purity grain that cuts cooler and lasts longer
Ideal for precision grinding on steels, hard alloys, and exotic materials
Ceramic Alumina
General-purpose deburring and blending
Commonly used on ferrous alloys, high-tensile steels, and wood
Diamond
Hardest abrasive available
Used for grinding and polishing ceramics, stone, and aluminum alloys
Silicon Carbide
Fast-cutting abrasive, harder than ceramic
Best for nonferrous metals and low-pressure applications
Tungsten Carbide
High wear resistance even at elevated temperatures
Works on ferrous and nonferrous materials, including cast iron, nickel alloys, and stainless steel
Zirconia Alumina
Durable and self-sharpening as grains fracture
Excellent for medium- to heavy-material removal
Common in carbon steels, aerospace alloys, nickel alloys, aluminum, and cast iron
Other Grinding Wheel Types

Bench and Pedestal Wheels
For sharpening, shaping, and deburring tools and parts (generally on stone and metal materials).

Centerless and Cylindrical Wheels
For finishing round workpieces held between centers or chucks or stock removal, always in combination with a feed wheel and a rest blade for support.

Cut-Off Wheels
For cutting, notching, and light grinding with portable or stationary tools for various materials (such as aluminum, plastic, and wood).

Tool and Cutter Wheels
For sharpening and fabricating cutting tools, including milling cutters and drills, in portable or stationary equipment (such as CNC machines).


Internal Grinding Wheels
For grinding inside diameters of bearings, cylinders, and compressors.


