Unlike lathes, where the workpiece rotates, milling machines use a rotating cutter to operate. Most models feature self-contained electric motors, coolant systems, digital readouts, variable spindle speeds, and power-driven table feeds. In addition to surface machining, they can also be used for drilling, boring, gear cutting, and creating slots or pockets.
Milling Machines: Types, Tips, and Accessories
Milling machines are used to machine solid materials like metal, plastic, and wood. They are especially effective for producing flat or irregular surfaces.
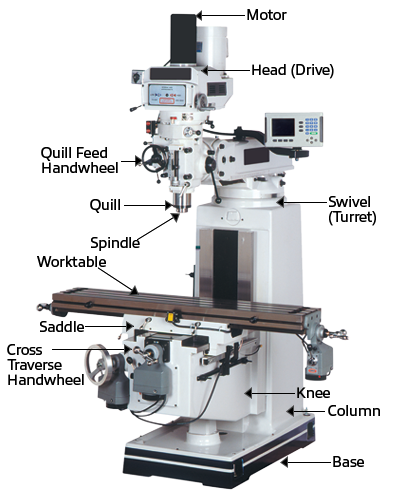
Diagram of a Milling Machine
Horizontal and Vertical Mills
Horizontal mills are designed so the cutters are mounted on a horizontal spindle. They are equipped with a rotary table, allowing for milling grooves, slots and other heavier cuts at several angles. They are commonly identified as a universal milling machine.
Vertical mills are designed with a spindle axis that is vertically oriented. The spindle can be extended, or the table raised and lowered, allowing for plunge cuts and drilling. There are two types of vertical mills:
- Bed mills, which have a fixed table and a head that moves in a Z-axis. This allows for additional weighted parts to be machined.
- Turret mills, which can be moved perpendicular and parallel to the spindle axis.
Milling Machines
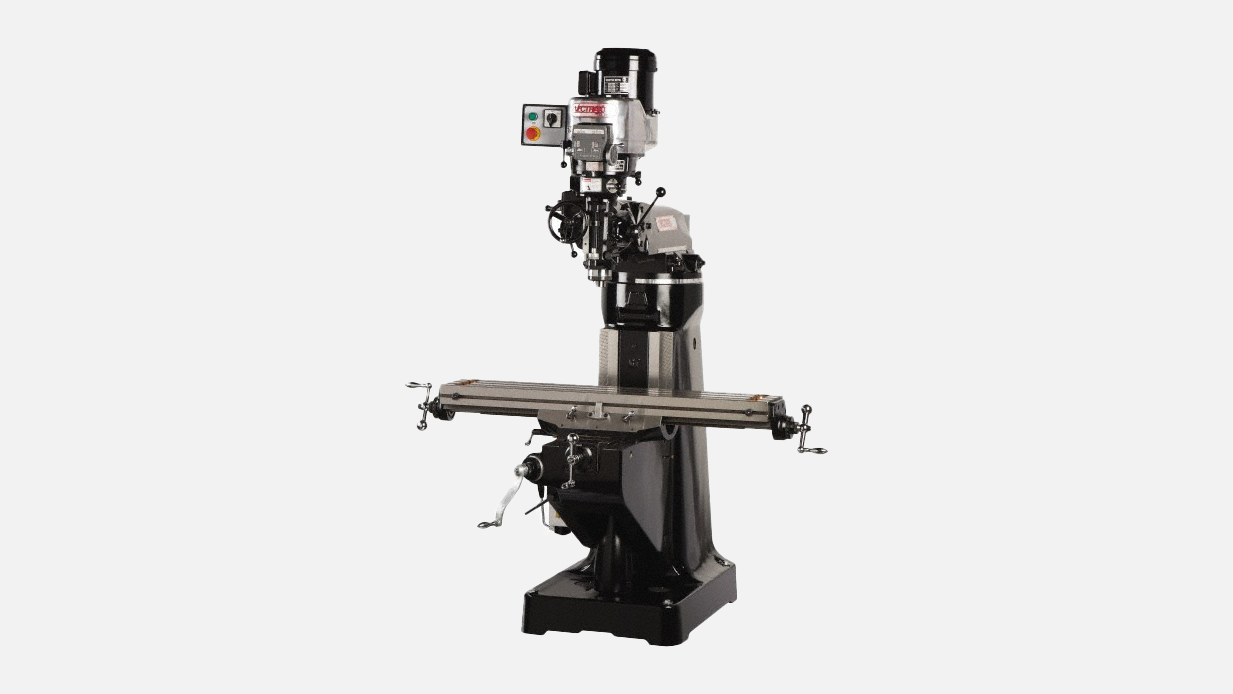

Knee Milling Machines
Knee milling machines are used to cut internal or external features of a workpiece using a rotating milling cutter. They support a wide range of operations, including milling, drilling, tapping, facing, keyway cutting, pocketing, and slotting. These machines feature a T-slotted worktable with three slots for securely clamping the material during machining.
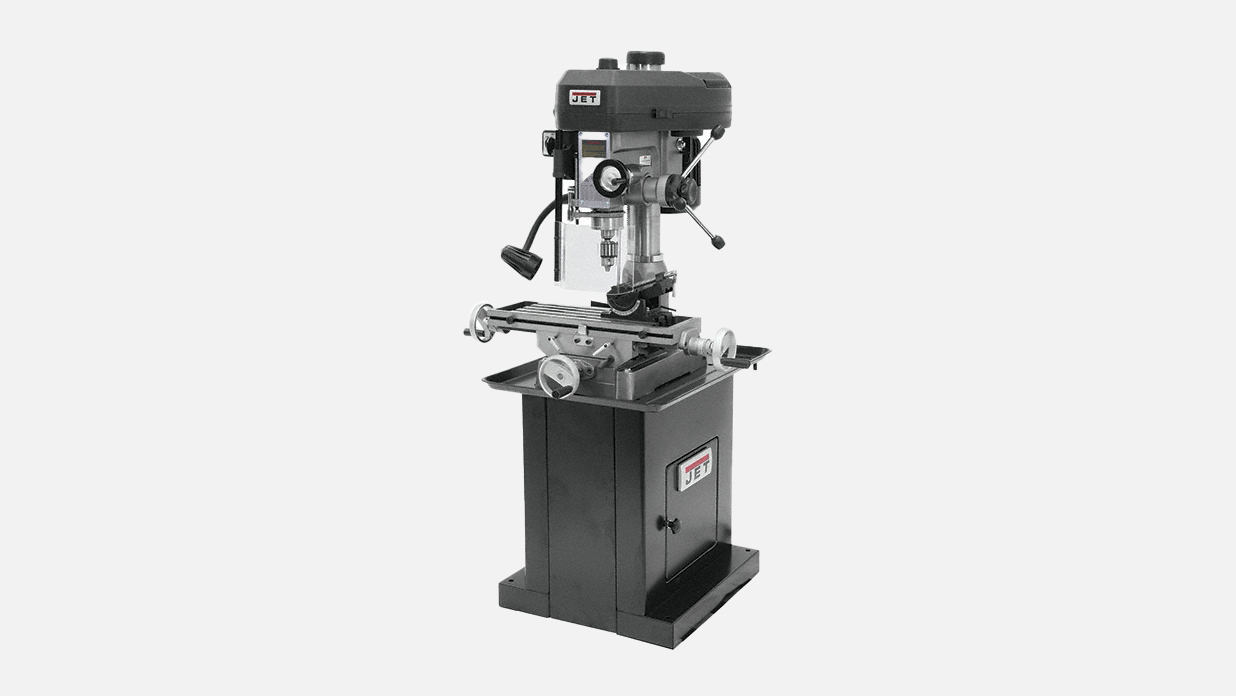

Mill Drill Machines
Mill drill machines are used for precise boring, drilling, milling, and tapping operations. They feature spindles capable of handling side-cutting loads and rigid milling tables with X-Y movement. Lightweight and compact, they are ideal for applications where space is limited.
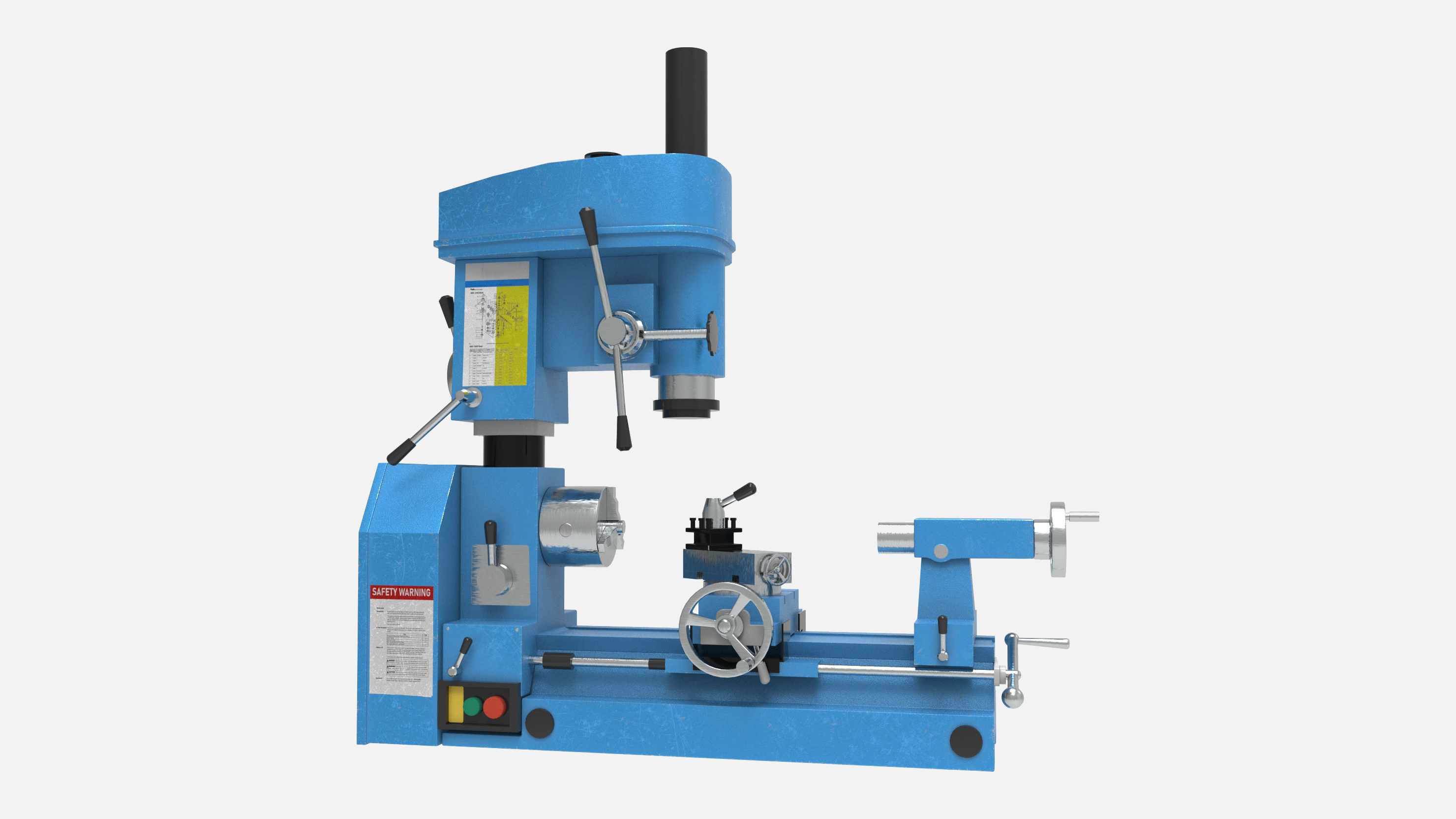

3-in-1 Machines
3-In-1 Machines combine milling, drilling, and lathing in one convenient unit.
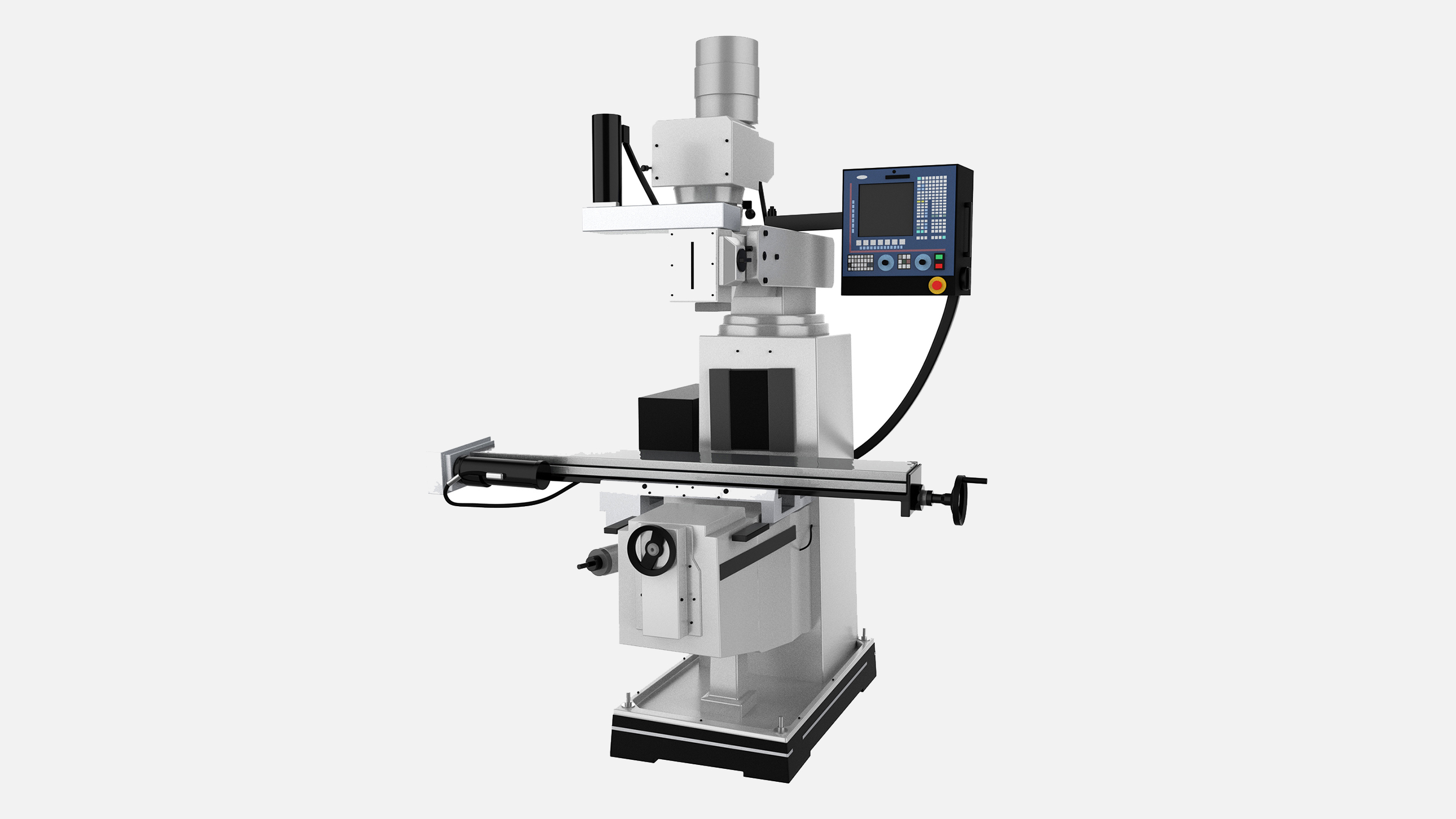

Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) Milling Machines
Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) milling machines use end mills to remove and shape material during milling operations. They are programmed with alphanumeric codes—commonly called G-codes—that direct the machine to follow specific cutting patterns or perform designated functions. CNC milling machines operate in 3- or 4-axis configurations, enabling vertical, cross, and longitudinal movement, as well as optional 4-axis rotary positioning.
Spindle Speed
Spindle speed control refers to the mechanism used to drive the spindle at a specified speed.
Step pulleys use a manually adjusted belt system to achieve specific spindle speeds, typically offering 8 or 16 fixed settings.
Variable speed pulleys use a cog-type belt system and a variable-speed assembly that allows continuous speed adjustment via a dial.
Electronic Variable Speed (EVS) systems feature unlimited speed options within the maximum and minimum speed ranges. The speed is controlled electronically rather than manually by turning a dial. EVS features several speeds within a specified speed range.
Geared head drive systems offer rapid speed changes by moving the gears in the head, providing three to four fixed speeds.
Terminology
Cross travel, also known as Y-axis travel, measures the maximum distance that the working surface moves in a forward-and-backward (in-and-out) motion.
Distance between centers refers to the measurement from the headstock center to the tailstock center, indicating the maximum length of a workpiece the machine can accommodate.
Knee travel, also known as Z-axis travel, measures the maximum distance that the working surface moves in an up-and-down (vertical) motion.
Longitudinal travel, also known as X-axis travel, measures the maximum distance that the working surface moves in a right-to-left (horizontal) motion.
Phase refers to how the current passes through the motor.
Single-phase refers to a power supply with one alternating current (AC) line that delivers voltage to the motor. It is generally less efficient than a three-phase power supply.
Three-phase refers to three individual lines (coils) that connect to and run voltage through the motor. Each line alternates in a sequence as it reaches its voltage peak. They provide a more stable flow of voltage and more horsepower to the equipment.
Travel distance indicates the measurement on the Y-axis (in-and-out) and X-axis (right-to-left, or horizontal) motion.
Table length refers to the measurement of the total table.
Table width refers to the measurement of the width of the table.

