A tape measure, also known as measuring tape, is a flexible, portable hand tool designed for measuring distances or sizes with precision. MSC Industrial Supply offers a variety of sizes to suit different needs. Wider tape measures tend to be sturdier and easier to read. Tape measure markings along the edge of the tape are typically in either inches and feet or centimeters and meters, depending on the model.
Understanding Tape Measures: Features & Benefits
Explore essential tape measure features like blade materials, readability, and key functions to ensure precision and efficiency in any measuring application.
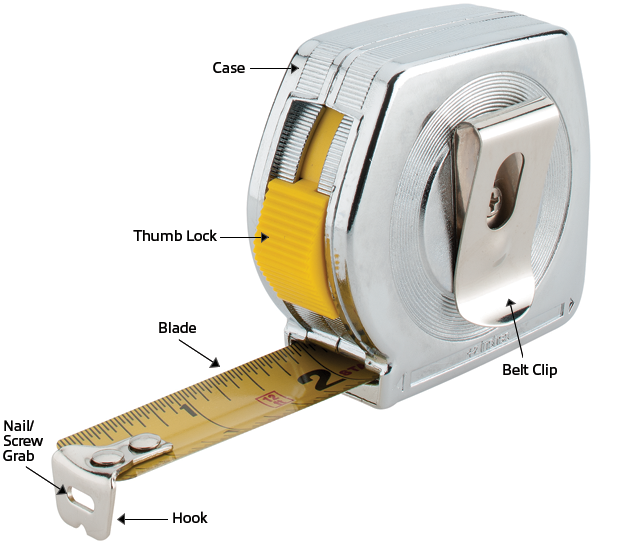
Diagram of a Tape Measure
Essential Tips
Attachment Point
Some tape measures are designed with an integrated through hole that can be used with a lanyard/tethered loop attachment. It is ideal for use in applications where height is a factor.
High Visibility
Tape measure marks and color play an important role in determining which tape best fits your needs. For increased visibility in applications where lighting is limited, select measuring tapes that have easily readable blades and markings.
Standout
The tape measure’s standout is the distance a blade can extend before bending. Wider blades typically extend further without any support. Many tape measures indicate the standout on the packaging.
Key Features of a Tape Measure
More Tape Measures from MSC Industrial Supply

Adhesive Tape Measure
Adhesive tape measures are used in applications where frequent measurements occur. They can be cut to any length and have an adhesive backing that allows for the tape to be placed on any surface.
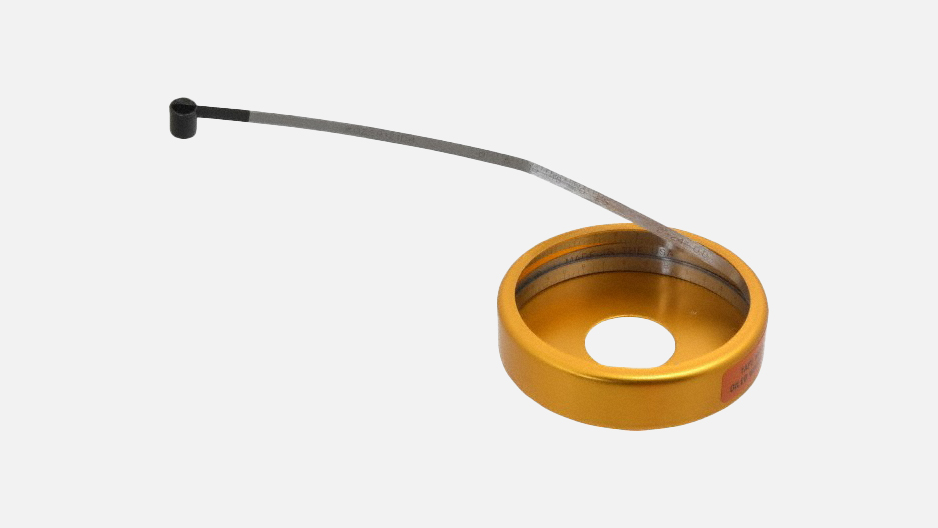

Spring Steel Diameter Tape Measure
Diameter tape measures are used for measuring circular objects like pipes and cables. They are designed so that zero falls in the same place on each side of the blade. The conversion from diameter to circumference is made by turning the blade. They make use of Pi, which is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
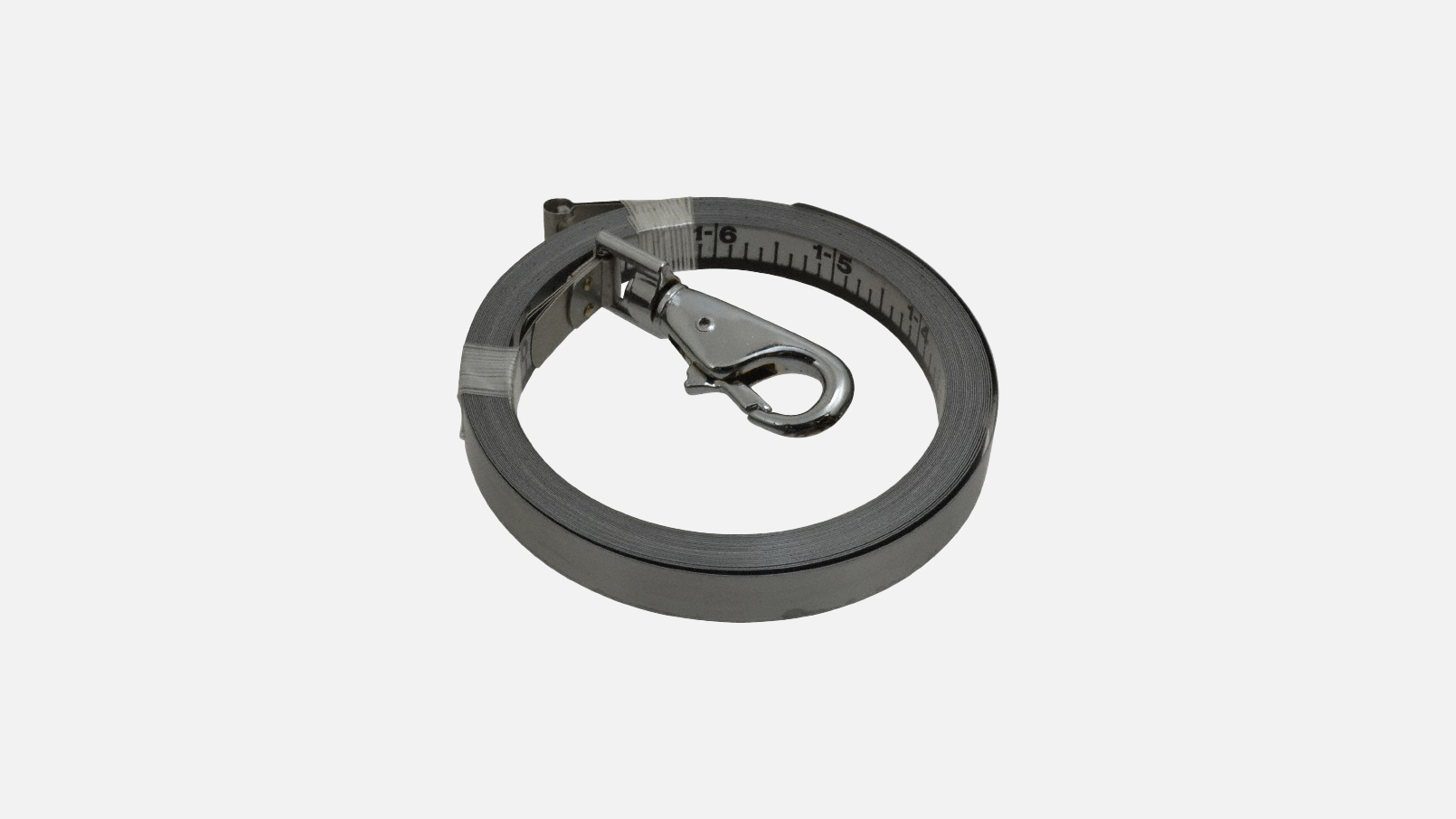

Tape Measure Replacement Blade
Tape measure replacement blades are ideal for when the blade breaks during an application. They are available in several styles.

